Master Server Configuration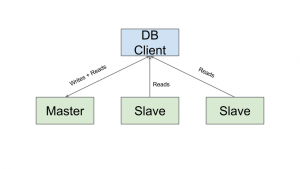
Install MySQL Server:
sudo apt-get install -y mysql-server
Add the following to /etc/mysql/my.conf:
bind-address = 10.11.12.101 server-id = 1 log_bin = /var/log/mysql/mysql-bin.log
Restart MySQL:
sudo service mysql restart
Create a replication user:
mysql -u root CREATE USER 'repl'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'slavepassword'; GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'repl'@'%'; exit
Create a snapshot and copy it to the slave server:
mysqldump -u root --all-databases --master-data > masterdump.sql scp masterdump.sql 10.11.12.102:
Slave Server Configuration
On the slave, install MySQL Server:
sudo apt-get install -y mysql-server
Add the following to /etc/mysql/my.conf:
bind-address = 10.11.12.102 server-id = 2
Restart MySQL:
sudo service mysql restart
Tell the slave what user, password, and host to use for the master server:
mysql -u root CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='10.11.12.101', MASTER_USER='repl', MASTER_PASSWORD='slavepassword'; exit
Restore the snapshot:
mysql -uroot < masterdump.sql
Start the slave:
mysql -u root start slave; show slave status\G;
Taking it to the next level… (Multimaster Clustering)
If you want to learn how to create a true multi-master MySQL database cluster, check out High Availability for the LAMP Stack.