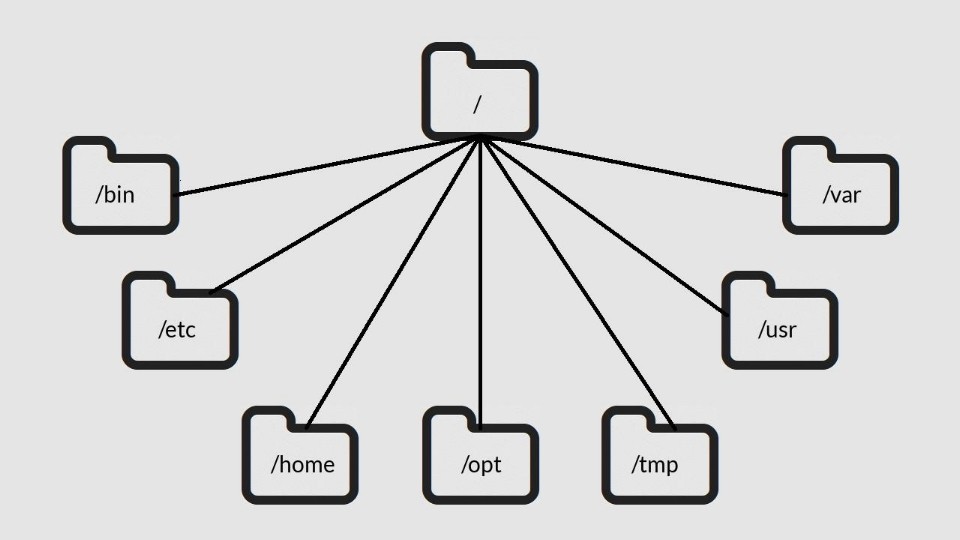
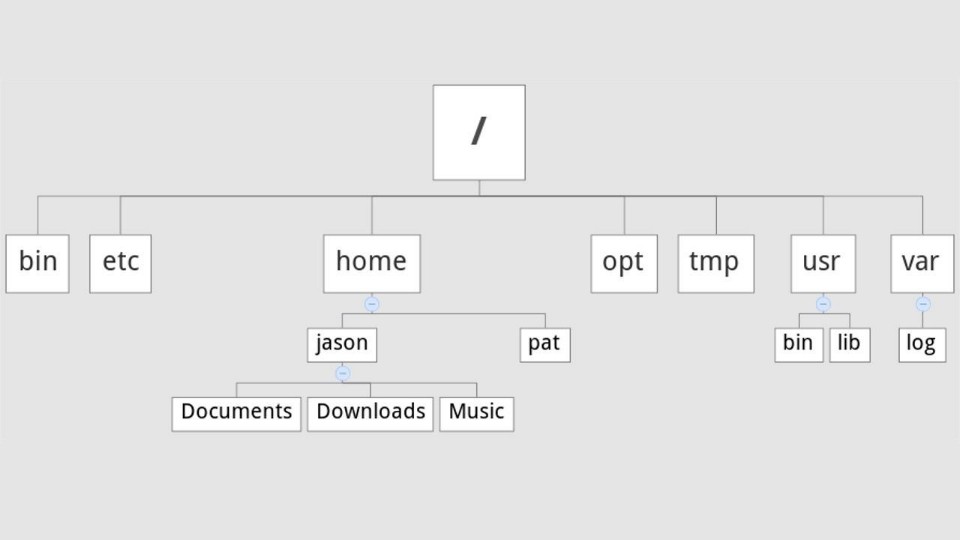
Common Top Level Directories
Here are the most common top level directories that you need to be aware of and may interact with as a user of a Linux system.
| Dir | Description |
|---|---|
/ | The directory called “root.” It is the starting point for the file system hierarchy. Note that this is not related to the root, or superuser, account. |
/bin | Binaries and other executable programs. |
/etc | System configuration files. |
/home | Home directories. |
/opt | Optional or third party software. |
/tmp | Temporary space, typically cleared on reboot. |
/usr | User related programs. |
/var | Variable data, most notably log files. |
The Linux directory structure is like a tree. The base of the Linux file system hierarchy begins at the root. Directories branch off the root, but everything starts at root.
The directory separator in Linux is the forward slash (/). When talking about directories and speaking directory paths, “forward slash” is abbreviated to “slash.” Often the root of the file system is referred to as “slash” since the full path to it is /. If you hear someone say “look in slash” or “that file is in slash,” they are referring to the root directory.
The /bin directory is where you will find binary or executable files. Programs are written in source code which is human readable text. Source code is then compiled into machine readable binaries. They are called binaries because machine code is a series of zeros and ones. The import thing to know is that commands, programs, and applications that you can use are sometimes located in /bin.
Configuration files live in the /etc directory. Configuration files control how the operating system or applications behave. For example, there is a file in /etc that tells the operating system whether to boot into a text mode or a graphical mode.
User home directories are located in /home. If your account name is “pat” your home directory will be /home/pat. Linux systems can and often do have multiple user accounts. Home directories allow each user to separate their data from the other users on the system. The pat directory is knows as a subdirectory. A subdirectory is simply a directory that resides inside another directory.
The /opt directory houses optional or third party software. Software that is not bundled with the operating system will often been installed in /opt. For example, the Google Earth application is not part of the standard Linux operating system and gets installed in the /opt/google/earth directory.
Temporary space is allocated in /tmp. Most Linux distributions clear the contents of /tmp at boot time. Be aware that if you put files in /tmp and the Linux system reboots, your files will more than likely be gone. The /tmp directory is a great place to store temporary files, but do not put anything in /tmp that you want to keep long term.
The /usr directory is called “user.” You will find user related binary programs and executables in the /usr/bin directory.
Variable data such as log files reside in /var. Specifically, the /var/log directory contains logs generated by the operating system and other applications.
These are only the most commonly used directories. For a more comprehensive listing and details see the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard.
For even more content like this…
If you enjoyed this article, you’ll definitely enjoy the Learn Linux in 5 Days course. Click here to learn more.